Product Development Tools to Use in 2025

In a genuinely competitive market today, industries need intelligence systems to innovate faster, collaborate better, and take less time to bring a product through to completion. Thus, the need for product development tools has become very much essential. Such tools enable teams to optimize workflows, maximize minimizing manual efforts, and hasten product development duration from idea inception to product launch. They also heavily go towards this product development realm iron chain for ideas capture, wireframing, prototyping, and structured communications. They are designing the bridge between strategy and execution to provide a seamless environment for cooperation.
With the rise in demand for digital-first experiences, strong collaborative development software is used to manage backlogs, track releases, and automate testing from management to release. This ultimately improves on-time product and product quality.
Product management tools are being leaned on in strategic planning and execution to clarify roadmaps and priorities so that teams remain aligned and can fully focus on delivering customer value.
Those who are well-versed in future development will, by definition, begin with traditional platforms, frameworks, and technologies. Thus, we will later see product development tools and techniques that every modern-day team should be aware of.
Table of Contents
Why Product Development Tools Matter in 2025?
| Section | Subsection | Details |
| 1. Importance of Product Development Tools | Competitive Advantage | Product development tools have become essential to maintaining a competitive edge due to evolved customer expectations and saturated markets demanding swift delivery of products of the highest quality. |
| Team Empowerment | The toolsets empower the teams to lessen human error, shorten delivery cycles, and promote continuous product improvement based on real-time feedback. | |
| 2. Shift to Modern Techniques | Strategic Alignment | Organizations now opt for modern product development techniques to align their processes with changing user needs. |
| Key Practices | Such techniques embrace iterative development, data-driven decisions, and early validation so as to ensure that no stage of product development is purposeless and ineffective. | |
| 3. Choosing the Right Tools | Complexity Management | Choosing the best product development tools allows a business organization to manage its complexities with ease. |
| Process Coverage | The tools facilitate the whole process: from concept generation through planning to test execution, all the way down to better traceability and quick turnaround into execution. | |
| 4. Investing in Product Development Software | Cross-Team Visibility | An investment in strong software for product development makes room for visibility across teams and departments. |
| Centralized Communication | The software ensures communications are centralized, version control is in place, and integration is supported along with other enterprise systems, resulting in smooth processes and high-quality assurance. | |
| 5. Enhancing Value through Services | External Expertise | With this added, specialized product development services serve to further enhance value. |
| Risk Reduction and Scalability | This external association facilitates the imparting of niche expertise with domain knowledge and tried and trusted frameworks that lessen risks and render greater scalability. |
Categories of Product Development Tools
The product journey, from the very inception of an idea to the actual launch, needs a whole arsenal of product development tools to ensure that each part of the production is done efficiently. In theory, these tools can be grouped according to what they do and where in the product lifecycle they contribute. Let us dissect them into categories to understand better how these tools actually support modern teams.
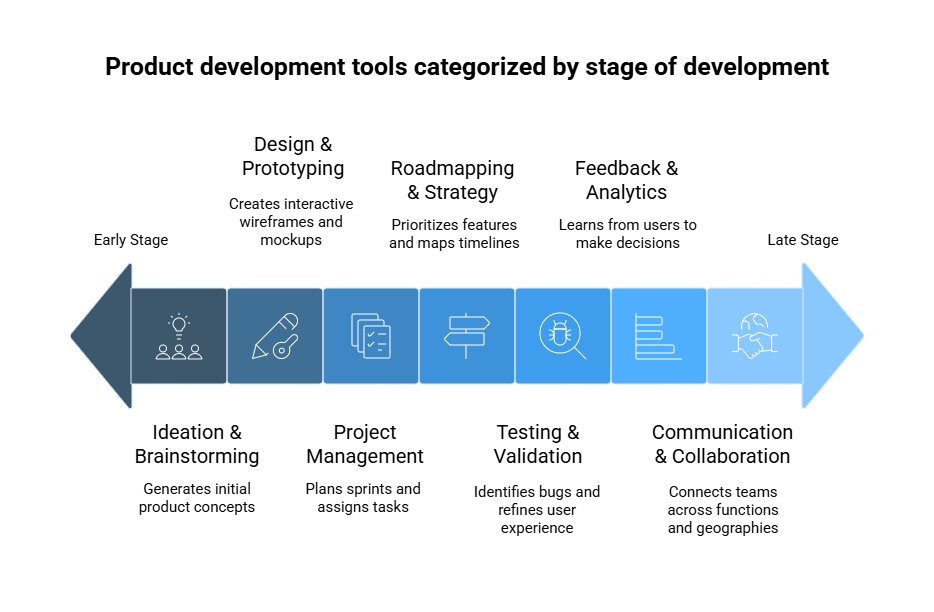
1. Ideation & Brainstorming
Ideas that ignite innovation. So, the teams use specific product development tools that can support visual thinking, whiteboarding, and mind mapping. However, platforms such as Miro and MindMeister allow stakeholders to work together to contribute, develop, and organize their thoughts and ideas, helping to convert such creative input into concrete product concepts.
2. Design & Prototyping
Visualization during the early stage is of paramount importance. Team members use product development tools like Figma, Adobe XD, and UXPin to create interactive wireframes and mockups. Through this work, designers simulate the user’s view of various iterations, thereby ensuring that the visual design is in accordance with the product goals that were set from the very start, prior to any kind of development.
3. Project Management and Task Tracking
Discipline is required. Teams use product management software such as Jira, Trello, and Asana to plan sprints, assign tasks, and monitor the progress of sprints. These platforms facilitate transparency across teams and maintain a universal set of priorities with respect to delivery timelines.
4. Road mapping & Strategy
Strategic alignment is as important as execution. Feature prioritization software like Aha!, Product board, and Roadmunk are used to maintain the strategic vision for the product, keep a view of the initiatives, and have timelines mapped out. These tools play a big part in agile product strategy, further channelled into prioritization based on customer and business value.
5. Testing & Validation
Quality is ensured via tester validation. Product teams use specialized product development testing tools, such as usability testing, A/B testing, and heatmap analysis, identifying bugs and points of friction while refining the UX. Hotjar and Maze, among others, fill a significant role in the context.
6. Feedback & Analytics
Feedback from customers results in an excellent product. When leveraging data from platforms such as Google Analytics and Mixpanel, meaningful product development methods are used. At the core of these methods lies the intent to learn from users in real time to make faster, evidence-based decisions.
7. Communication and Collaboration
We cannot complete the toolbox without perfect communication among the team. Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Zoom connect the dots across functions and geographies. These solutions are widely embraced in modern digital product engineering to bridge gaps among remote teams and cross-functional counterparts.
Launch Your Product with Our Experts
Top 15 Product Development Tools in 2025
The year 2025 will need organizations to employ succinct product development tools that will be able to streamline their operations for a creative approach to innovation and ensure the products are marketable. The fifteen tools mentioned below form a balanced toolkit across all segments, design, project management, testing, feedback, roadmapping, and communications.
1. Figma – Collaborative Design and Prototyping
For product development, especially in design and prototyping, Figma is probably one of the most widely used tools. This tool allows real-time collaboration amongst designers, developers, and stakeholders who work together in an ad-hoc fashion on wireframes or UI mockups in the same workspace.
2. UXPin – Advanced UX Design
UXPin is a product development software that allows teams to craft interactive code-based prototypes with logic and conditions. It reduces challenges related to handoff and supports dynamic design systems in the creation of scalable digital experiences.
3. Miro – Ideation & Whiteboarding Tool
Miro is considered one of the most intuitive product management tools for brainstorming, planning, and concept mapping in the early stages of the project. It is used by teams that require alignment around user journeys, customer personas, and backlog priorities.
4. Jira – End-to-End Project Management
Jira is the gold standard among Agile operations and the most used product development platform for Jira. It facilitates sprint planning, backlog grooming, bug tracking, and real-time reporting; hence, it is very central for engineering and product teams.
5. Productboard – Feature Prioritization and Roadmapping
Productboard links customer feedback directly to feature ideas, thus enabling teams to make better product decisions. It empowers product management in IT, effectively translating insights into prioritized initiatives.
6. Aha! – Strategic Planning
Aha! is a very capable roadmapping tool for planning, goal setting, and release tracking. It works quite well to bridge structured product development tools into techniques applied in strategic product decisions.
7. Trello – Visual Task Management
Trello is an easy Kanban-style task management tool. It keeps track of tasks and aligns teamwork. For teams just starting with structured product development techniques, Trello is a great steppingstone.
8. Adobe XD – Visual Mockups
For high-fidelity UI/UX mockups, Adobe XD is preferred. It provides design-to-code handoffs and integrates well with Creative Cloud. It is widely used within a number of custom product design services to enhance design workflows.
9. Hotjar – Behavior Analysis
Hotjar gives visual analytics through heatmaps, session recordings, and user polls. It works along with other new product development processes to provide data-driven insight into the functioning of their users with digital products.
10. Notion – Centralized Knowledge Base
Notion empowers organizations by allowing teams to organize notes, plans, and documentation, including their internal wiki. Therefore, it will act as a bridge between ideation and action by providing an easy-to-navigate structure to present content for modern-day product development tools.
11. Asana – Task & Project Tracking
Asana is a platform for cross-functional teams that is highly flexible in managing tasks, dependencies, and goals. Because it is easy to operate and integrate, it is one of the widely used tools for product development.
12. Maze – Rapid User Testing
Maze is a remote testing platform that lets teams test designs and collect feedback in a snap. It is a must-have product development tool that validates prototyping and optimization after launch.
13. Mixpanel – Product Analytics
Mixpanel supports deep analysis of user behaviour with retention and engagement metrics. It is the most powerful tool used in product management from a data-driven perspective.
14. Roadmunk – Product Roadmapping
Roadmunk permits product teams to develop visual, collaborative roadmaps that are aligned with company goals. It supports prioritization and strategy, and smaller integrations are handy for Jira in product development.
15. Slack – Team Communication
Slack uses seamless communication for teams working remotely or hybrid. It assists product management practices that are agile with fast updates, decision-making, or asynchronous workflows.
Benefits of Using the Right Product Development Tools
The correct set of product development tools is no longer an option; these are foundational for producing quality products that meet market expectations and are able to deliver value swiftly. Everything from the output of a team to customer satisfaction can be affected by these tools, and the benefits apply throughout the product’s life cycle.
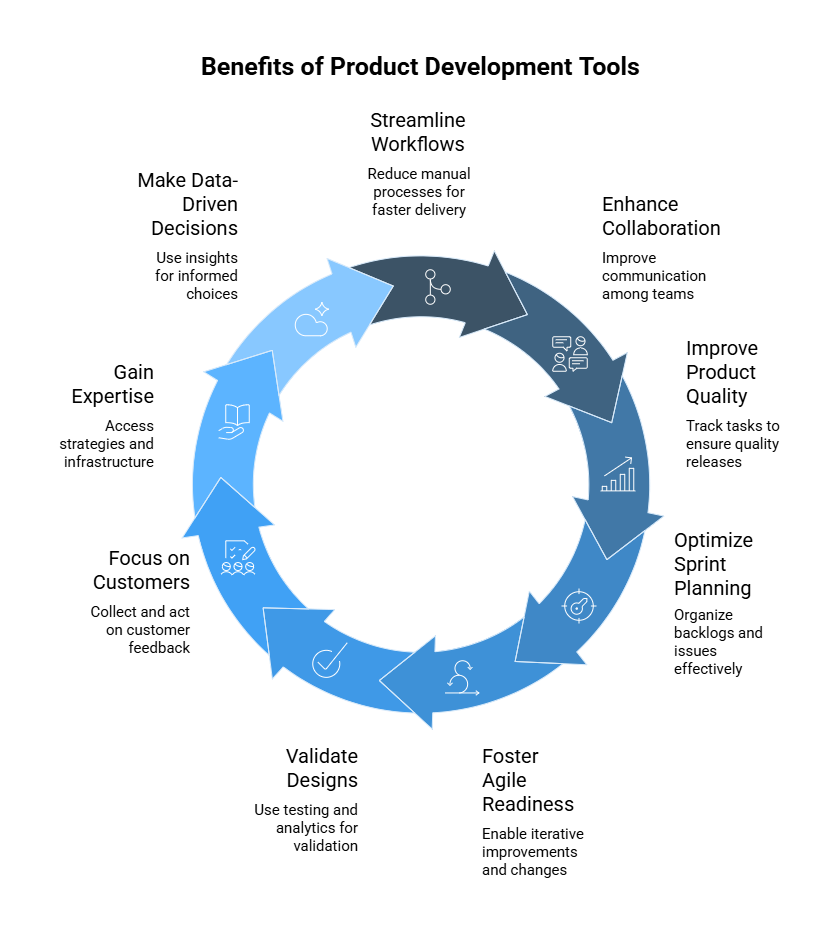
1. Streamlined Workflows and Faster Deliveries
One of the most significant advantages that a modern tool offers in product development is the ability to streamline fragmented workflows. Teams cut back time spent on manual processes so that they can move about ideation, prototyping, testing, and deployment with more speed and control.
2. Increased Collaboration among Teams
When software product design operates centrally within an organization, communication tends to become more seamless. Designers, developers, product managers, and stakeholders can all formally remain in sync regarding timelines, tasks, and deliverables, thus crushing silos and project delays.
3. Greater Quality Products with Fewer Bugs
Many teams use this kind of product management tool to track every task, feature, or bug from assignment to completion to delivery. The tools provide visibility and transparency, which in turn leads to higher-quality releases and fewer surprises after the product hits the market.
4. Better Sprint Planning and Execution
Using a tool like Jira or Confluence is a core part of Jira for product development best practice. These tools allow the organization of backlogs, assigning issues, and reviewing sprint velocity: all are critical points towards keeping a team on track and measuring how well they perform.
5. Agile Readiness/Iterative Improvements
It’s because of the movement towards iterative forms of delivery that sprint planning has become the foremost dominant form. Agile-based tools give the ability for teams to challenge assumptions rapidly and release them in small chunks, allowing for critical changes without threatening the overall strategy.
6. Set Up Better Validation and Feedback Loops
This generation of tools supports heat mapping, usability testing, A-B testing, and real-time analytics. Teams will be able to validate designs better and features much earlier in the development cycle than before, preventing costly rework.
7. Customer Focus
Customer-centric design emerges from correct product development usage. Such usage, when combined with the right platforms, assists teams in collecting, interpreting, and acting on end-user feedback throughout the product life cycle, not change post-launch.
8. Access to Niche Expertise
When companies work with product development organizations, they gain access to tested strategies, scalable infrastructure, and a vast cross-industry experience. Usually, this allows for the introduction of tool stacks along with frameworks that improve team velocity and reduce risk.
9. Real-Time Insight-Driven Decision-Making
Data-driven product development allows companies to gain insight into their customers’ most valued objects. The tools track engagement, retention, and conversion rates, enabling the team to make changes to priority lists based on insights rather than educated guesses.
Bring Your Product Idea to Life
Integrating Agile Product Management with Product Development Tools
Agile is no longer just a software development methodology. It has become the mindset adapted by various sectors to improve response, collaboration, and continuous improvements. For Agile to work successfully, team members should reflect their workflows on a product-development suite that promotes quick iterations, fast feedback, and maximum adaptability.
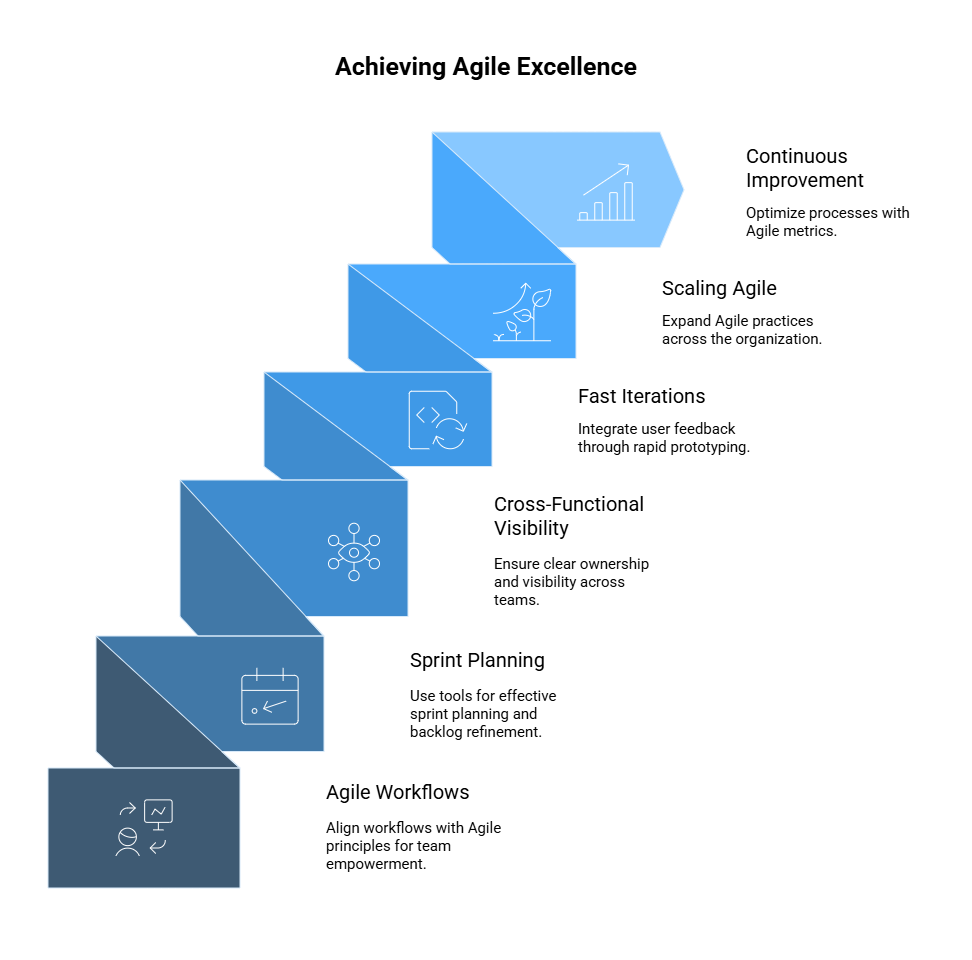
1. Agile Workflows and Tool Alignment
When agile workflow principles are applied to the product development lifecycle, it empowers the teams to have the ability to change without loss of momentum. Tools supporting Agile project management, such as Scrum boards, burndown charts, and backlog prioritization, are needed to keep the project moving quickly and clearly.
2. Sprint Planning and Backlog Refinement
Because of tools like Jira, Trello, and Asana, Jira has thus become very popular among Agile teams for product development. These tools assist with sprint planning, managing epics and stories, and product backlog refinement as priorities change, and user feedback is received.
3. Cross-Functional Visibility and Accountability
Successful Agile execution also requires clear ownership and visibility. Many teams use various product development tools and practices such as story mapping, Kanban boards, and integrated retrospectives and metrics to track performance and pinpoint areas for process improvement.
4. Fast Iterations and Integration of User Feedback
Agile teams rely on tried-and-true product development methodologies to test assumptions early and often. These practices, such as MVP releases, rapid prototyping, and tight feedback loops, make sure that user input is integrated into every sprint rather than being inserted after launch.
5. Scaling Agile with Tooling Support
Whether you are managing a single team or scaling across many teams, coupling structured frameworks with modern product development services serves to scale Agile across the organization. These services often come with recommendations for tooling and integration strategies relevant to your current stage of product maturity.
6. Continuous Improvement and Agile Metrics
With the proper product development methods, Agile stops becoming a buzzword and becomes a measurable, repeatable process. Velocity, cycle time, and customer satisfaction are some of the metrics Agile tooling tracks to optimize continuously.
Choosing the Right Product Development Tools for Long-term Success
Product development tools define how well a team can innovate, scale, and deliver efficiently. It’s not just about the specifications but rather about aligning strategy, ease of use, scalability capabilities, integration prowess, and overall return on investment with the company’s long-term business goals.
1. Strategy Alignment
Every business faces its unique set of challenges, and the product development tools chosen to address those challenges should reflect the approach. Selecting the right product development tools begins by defining what your team is trying to achieve at a fundamental level. It can be speed, collaboration, or quality- a tool to help with any of these needs is the tool to use. If a toolset is not aligned with your business strategy, it may instead create friction, slow momentum, or add unnecessary layers of complexity. Thus, start by identifying the pain points your team faces and picking your tools accordingly.
2. Ease of Use and Adoption
Whatever features a platform might offer, if your team cannot use it, then it isn’t very helpful. UX is the key to tool adoption. The interface design should emphasize ease of use while onboarding processes are kept simple so it can easily glide through day-to-day tasks. If the product-development tools require large amounts of training time for basic navigation or a complicated setup, then adoption is guaranteed to fail. Always run pilot programs before anything is placed into full commitment and then use feedback from end-users as to whether the tool really does fit into their working methods.
3. Scalability for Growth
Teams change, projects grow, and organizational architectures evolve. Product development tools should serve the team up to one year or even five years from now. On the other hand, tools that scale in tandem with your business evolution will help to limit disruptions and cost-inhibiting migrations in the future. Look for one that has modular features paired with flexible pricing models anytime. It can be an enterprise-ready tool that is able to support little teams alongside large, multi-department organizations. Basically, they will grow with you rather than hold you back.
4. Seamless Integration
In the current environment of development, tools do not work in silos, so to speak. Your whole product ecosystem must be connected from the design system to your customer feedback channels. Hence, integration is a deal breaker when selecting product development tools. Take the best tool that can plug into your current stack with a minimum amount of configuration. Whether it sync data from a task board, push new updates to customers’ records, or connects design assets, tools must start talking to each other to streamline processes and reduce manual work.
5. Return on Investment
While costs matter, value shall be of prime importance. There may be cheaper software that eventually would cost you a whole lot more due to inefficiencies that it produces, rework, or poor coordination among the team. Judge the product development tools according to the actual results they deliver, whether fast delivery, less-error-prone scenarios, good collaboration, or increased customer satisfaction. If a tool significantly contributes to any one of these results, it is worth the investment.
Future Trends in Product Development Tools
Technological advances are shaping the rise of innovative, fast, collaborative product development tools. Given their nature, the next generation of tools can really transform how teams design, build, and deliver their products, thereby creating an environment where innovation is easily made, and product cycles are more adaptive.
1. AI Decision-Making
Artificial Intelligence deployment has entered several product lifecycle environments. Emerging systems track and analyze usage patterns, anticipate user needs, and advise prioritization of features. Instead of relying on presumed intuition or logical experience, product teams can set a precedent of legitimacy, and confirmation comes from conclusive data generated by intelligent systems. From AI-generated test cases to recommendations for interface improvements, AI applications in product management seem more pre-emptive than reactive. The more innovative product teams work, the faster product development becomes standard with tools that once were optional.
2. Real-Time Cross-Functional Collaboration
Remote-work culture has truly placed collaboration at the forefront of hierarchies. Future product development tools are being designed with features of real-time syncing, immediate feedback, and smooth communication across platforms. Tools that were once specific to one domain, such as design or engineering, are now becoming one centralized platform for the entire product team. Whether co-editing on an interface, tracking live updates, or sharing customer insights, real-time collaboration eliminates delays and keeps everyone aligned across time zones.
3. No-Code and Low-Code Expansion
The rise of no-code and low-code platforms is currently democratizing product development. Such platforms empower the non-technical members of the team to join the collaborative creation of workflows, automation, and even working prototypes. Product Managers, marketers, and designers no longer need an engineer’s bandwidth for minor changes or experiments. This evolution in the field allows for a much speedier phase of experimentation and draws in a much wider group of collaborators. In the next few years, we can expect that more product development tools will embrace two-thirds of the current no-code movement to minimize bottlenecks and allow input from cross-functional teams.
4. Integrated Product Analytics
Knowing what the users want is equally essential as delivering features. That is why product development tools of the future embed product analytics right into the product development process. Teams no longer must wait for the product to be launched before they can have a clue as to how it is doing. Through integrated analytics, designers and developers will also be able to track feature engagement, retention metrics, and conversion rates, all in real time, easing the iterations and improving customer satisfaction.
5. Cloud-Native and API-First Architecture
The product teams definitely demand more flexible and interoperable systems. Hence, future product development tools are being built on cloud-native infrastructures with API-first design. The design-topology allows quicker deployment, better scalability, and easy integration across increasing numbers of platforms. Based on the workflows, teams can assemble their own toolchain rather than being stuck to rigid suites. They also help API-first tools stay ready for what’s next by adapting to emerging technologies.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Adopting Product Development Tools
Many teams rush into adopting new platforms with high expectations. However, the best product development tool can become a bottleneck for inefficiency without due process. Making sure the usual implementation missteps are avoided is your best chance of getting the most value out of your investment.
1. Choosing Tools Based on Hype, Not Needs
It’s tempting to let unlikely buzzwords tempt you into the latest trends from the tech space. However, a popular tool is not necessarily a tool for your team. Any product development tool adoption must always start with analyzing needs. What problems are you trying to solve? Who will use the tool regularly in a day? How will it fit into your daily routine? When these questions are not answered upfront, the tool tends to be a waste of budget and bring low engagement levels to the teams.
2. Not Honoring Team Involvement in The Evaluation Process
Selecting a tool is not only a decision for IT or leadership; it touches upon everyone who goes through a product’s professional life cycle. The one most common error is to leave crucial team members in the evaluation stage. Developers, designers, product managers, and QAs should all help with testing trials and give feedback. If the tools you picked don’t fit well in your team’s culture, they will probably face some resistance or may even get used very little at all.
3. Rolling Out Too Many Tools Simultaneously
Rolling out several new tools to your team simultaneously will create confusion and burnout among them. Try to apply a new tool for every problem you see, but this method will do more harm than good. Therefore, stagger the adoption process so teams can acclimatize. This also prevents redundancy and reduces frustration since you’d have already had the opportunity to evaluate which tools actually provide value in your product development process before introducing others.
4. Failing to Provide Training or Documentation
Assuming they will just “figure it out” is a cardinal sin. Again, Even the intuitive tools require some degree of onboarding. Without training sessions, adequate documentation, or even designated support, your team will fall back into their old ways or will wrongly implement these tools. The successful adoption of product development tools not only envisages initial training but also continued resources as an ongoing basis to support team-member efficiency throughout the adoption process.
5. Not Assigning Ownership and Governance
Hi, interchange with setups, and maintain your speedy tool optimization so there will be no time when things will be broken. It means inconsistency in workflows, chaotic permissions, and broken integration. Assigning a definite owner or dividing the administrative duty among a few internal teams guarantees that the tools are functional, secure, and ready to meet the needs of the company. Apart from this, ownership means someone would be actively seeking feedback from the company to implement improvements.
6. Ignoring Post-Adoption Metrics
In most road maps, lately, most parties have ignored the impact since its implementation. It is indeed, though, as much measuring success as is setup. Do team members use it? Does it accelerate speed or improve quality and transparency? If it doesn’t work out, you may want to rethink your strategy. Product development tools should be tracked regularly to ensure they are adding value to business objectives, just noise.
How Product Development Tools Support Remote and Hybrid Teams
Remote and hybrid work models have somewhat changed business operations for product teams. In the absence of physical proximity, digital systems now have to bear heavy lifting. Product development tools hold distributed teams together, ensuring alignment, productivity, and concentration, irrespective of where they are working.
1. Real-Time Visibility for Distributed Workflows
With members located in different locations and time zones, visibility of workstreams is key. Dashboards, activity feeds, and live updates ensure that everyone sees the status of projects as they evolve. Product development tools allow remote teams to easily track progress and identify bottlenecks or action items without direct checks or meetings.
2. Centralized Access to Product Information
Information may rapidly turn into silos in hybrid environments. Everyone needs an enterable and searchable structured system where documents, roadmaps, designs, and feedback live. The ideal product development tool offers an organized and searchable space to store everything relating to the product. This helps eradicate confusion and guarantees all stakeholders have access to the most recent and accurate information.
3. Asynchronous Communication and Updates
Collaboration does not need to happen in real time. There are some occasions for distributed teams to collaborate asynchronously to prevent disturbances in working intensely or to ensure conflicts with other time zones are avoided. Product development software aids by allowing workers to comment on tasks, track changes with version history, and maintain in-app conversations over time. Together, these features allow less reliance on live meetings and emails while keeping everyone in the loop.
4. Shared Ownership and Accountability
Without random actions and in-person check-ins, accountability needs to be baked right into the workflow. Product development tools support managers and contributors in assigning tasks, setting due dates, and openly tracking ownership. Anyone can view what has been completed, what remains to be done, and who is responsible for each item without needing to chase people down for status updates.
5. Better Collaboration Through Integrations
The teams nowadays employ a kaleidoscope of software to get through their workforces, designing, coding, steering customer insights, and analyzing the data. The best product development tools allow for integrations that fuse these components into one single workflow. The resulting integration forms a good user experience path all across the toolchain for remote teams, saving time and getting away from manual labor
6. Reduced Onboarding Time for New Hires
Remote teams often grow fast and make hires globally. Onboarding new members can make things challenging for anyone when processes are not documented or tools are not standardized. Product development tools help fix this by sculpting a consistent template that new hires can more easily grasp. From workflow documentation to shared templates, these platforms decrease ramp-up time and maintain continuity.
Conclusion
Product development tools are the foundation for building efficient, collaborative, and future-ready product teams. Properly thought-out and implemented, they streamline workflows, improve visibility, and foster innovation across the entire product lifecycle. However, they won’t add value unless they are appropriate to your team’s needs and goals. Avoiding common adoption pitfalls and planning for scalability guarantees impact over the long haul.
If you are looking for product development services, you can visit here.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the most important tools for product development today?
For product development, the tools can include task management, collaboration, prototyping, testing, and user feedback-type tools. Tools such as Jira, Figma, Hotjar, and Trello assist in streamlining the development process from ideation to launch. Product development tools should be chosen depending on their team size, workflows, and product complexity.
Q: How does product development software differ from traditional project management tools?
Product development software is designed to deal with all stages of product development life cycle activities from planning to prototyping, to user feedback, to testing, to iteration. On the other hand, generic project tools do not tend to have any of the product-oriented features for product strategies, roadmap definitions, and cross-functional communications that are necessary to build and develop customer-facing products.
Q: What are product management tools used for?
Product management tools help teams prioritize features, draw product roadmaps and track customer feedback, bringing business goals to alignment with development. A product manager in need of insight from both technical progress and customer requirements finds these tools indispensable; with the best product planning software, transparency is promoted, decisions are made through data, and communication among stakeholders is improved.
Q: Why is Jira popular for product development?
Product developments made in Jira are favored because they allow agile workflows, sprint planning, backlog management, and granular issue tracking. Software development teams especially revere it for its flexibility, scalability, and third-party integrations. Whether from a developer or a product owner perspective, this tool structure aligns with customizability to help align development teams toward product goals.
Q: What is agile product management, and how does it work?
Agile product management is an iterative approach focused on the rapid delivery of customer value via minor, continuous enhancements. This approach foresees short cycles of development, constant feedback, and flexible planning. Agile roadmap essentially allows teams to embrace change, react swiftly to user feedback, and prioritize real-time insights.



