Microsoft Power Apps: What It Is and How It Works?

Microsoft Power Apps is a great low-code/no-code application development tool that enables companies to quickly and easily build custom apps without having a strong knowledge of the programming language and hence avoids the use of a lot of code development. It is a sub-Cottage Industry of Microsoft Power Platform, equipping both developers and non-developers to create any type of solutions to address unique business challenges arising from the working environment, with the aim of simplifying operations and productivity.
In this fast-paced digital era, companies crave flexible tools that can evolve with changing needs. Offering a powerful user interface layered with pre-built templates and integration points with both Microsoft and third-party services, Power Apps has never made it easier to create web or mobile applications. This hybrid nature of being able to connect and integrate with varied data sources from Microsoft 365 to a SQL database makes your applications powerful from both functional and data richness perspectives.
In this article, we shall expound on what Power Apps is, how it works, the key features it offers, the benefits it brings to the business, and the position it holds in the Microsoft ecosystem. By the end of this article, you shall understand how and why this platform is fast becoming the preferred platform with organizations because they want to move faster in innovation and channel more empowered resources to build solutions.
Table of Contents
What is Power Apps?
When one asks “What is Power Apps?” The connotation is usually with reference to a Microsoft-product that allows applications to be built at a rapid speed. In a way, Power Apps create a barrier-less domain of application development, thereby enabling users with varying technical competency levels to build professional-gratification solutions that are concurrently operable on the web or on mobile platforms.
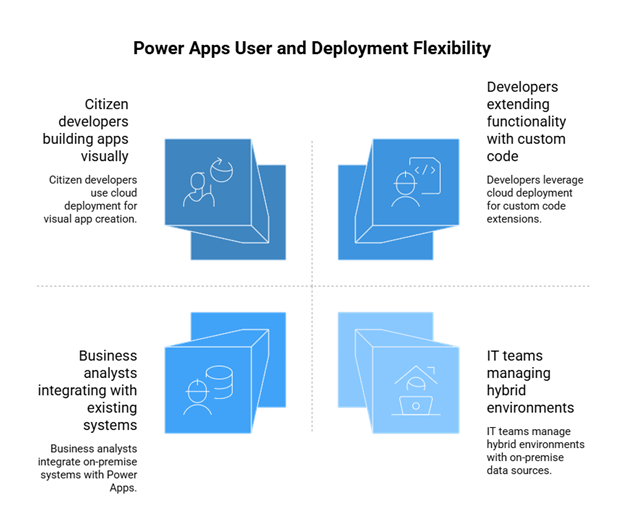
Definition and Conceptual Meaning
At the gravamen, Power Apps are a suite of applications and services, along with a set of connectors and a data platform, that allows rapid application development. The intent for designing it is to make the process of building apps feel as simple as drag-and-drop on a canvas.
Within the Microsoft Power Platform
Power Apps sits on the Power Platform alongside Power BI, Power Automate, and Power Virtual Agents as one of four key products. It serves as the center for app creation where they can digitize processes and increase workflow efficiencies.
Low-Code or No-Code Environment
Fundamentally, this is what puts Microsoft Power Apps into a low-code/no-code toolbox-the ability to allow citizen developers to go all the way to build sophisticated apps without having to have extensive coding skills and thus freeing potential build work from existing IT teams that are already stretched thin.
Deployment: Cloud or On-Premise
Power Apps will give you flexibility, be it in the cloud, or over-side with on-premise data sources. The Pro software is extremely easy to integrate with existing systems, enabling hybrid environments wherever needed for best comparison.
Targeted Users
With Power Apps, developers are therefore considered a target population, but in addition to them, the business analysts and citizen developers also constitute the major potential audience of this software. The developers can extend their functionality by writing custom code, while the non-technical users can build functional apps using the visual tools available to them.
Reason for the Adoption
Really, it delivers value in what can be measured in faster timelines for development, cost-effectiveness, engagement of a broader section of the human resources in innovation. Businesses are able to create apps specific to their bespoke processes, with very small time intervals when compared to the typical software development route.
Build Apps Faster with Power Apps
What are the Key Power Apps Features?
Microsoft Power Apps gives a collection of features that let an organization scale, secure, and create an application in a user-friendly way, without too much programming. From AI integration to the union of data sources, applications built using these technologies allow businesses to implement functional solutions whose needs evolve with them, thus working in a multiplatform environment.
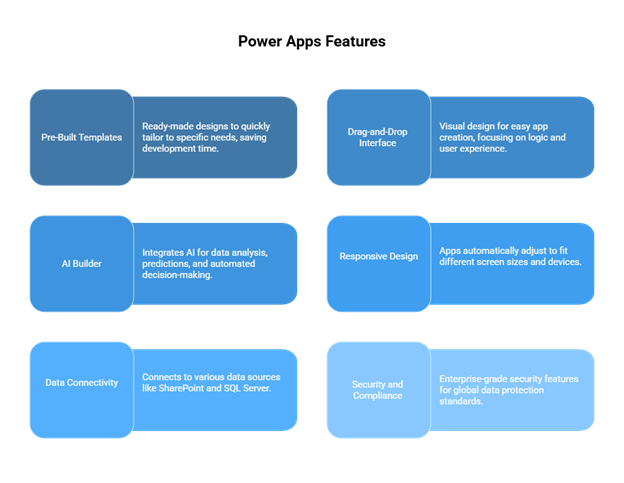
Pre-Built Templates
Among the biggest time-saving features of Power Apps is its range of pre-built templates. These templates allow users to take a proven design and tailor it to their exact needs, thereby limiting the amount of development time required.
Drag-and-Drop Interface
Would-be developers and the general public alike can design applications visually, thanks to the easy drag-and-drop builder. Thus, Microsoft’s solution empowers app designers to concentrate on business logic and UX instead of programming complexities.
AI Builder in Power Apps
The AI Builder inside Power Apps enables application builders to implement AI into their applications with no programming. It can analyze data, predict results, and automate decision-making actions so that applications act smarter and behave more responsively.
Responsive Design
Applications built with Microsoft Power Apps will adjust by themselves to fit the size of the screen at hand and the type of device that is being used. So, users will have an equal experience upon using the app on their desktop, on a tablet, or on their mobile phone.
Data Connectivity
With more than 500 connectors available, Power Apps can connect to a large pool of data sources such as SharePoint, Dynamics 365, SQL Server, and third-party applications. This big connectivity helps in bringing business data together and streamlining processes.
Security and Compliance
It is because of enterprise-grade security features that Microsoft’s Power Apps can be used by companies around the world, whether large or small. For every role, access is given, it complies with all data protection standards across the globe, and it is reasonably integrated within Microsoft’s security framework in order to best protect sensitive information.
How Power Apps Work?
Power Apps can unleash a variety of possibilities, and when one understands how the system works, he may realize its full power. Microsoft Power Apps brings together data connectivity, a visual design interface, and automation tools to generate applications that solve particular business needs. This streamlined approach allows teams to go from idea to deployment in rrapid time.
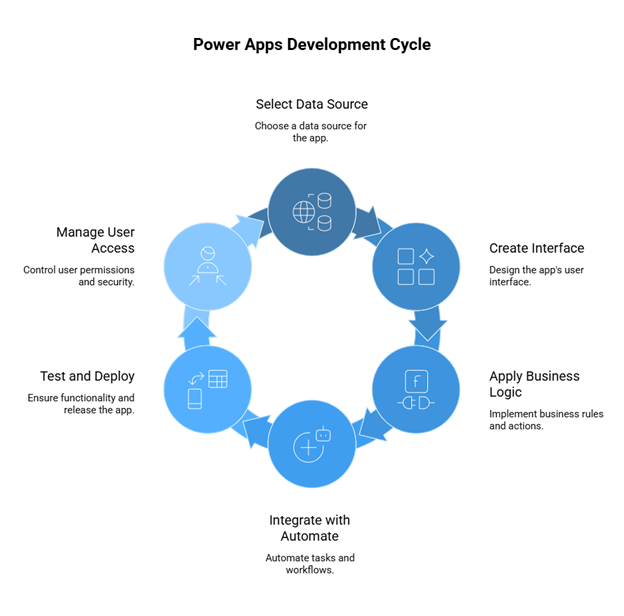
Selecting a Data Source
Every Power Apps application begins with a data source connecting to the backbone of storing and retrieving information: Could be Microsoft Dataverse as a strong data environment, SharePoint for collaborative document storage, SQL Server for an enterprise-grade database, or even some third-party platform via a given connector. Power Apps support-cloud-based-and on-premise data connections, presenting a versatile option suitable for a diverse range of IT infrastructures. This means a business can embed Microsoft Power Apps into their existing technology stack without having to rip everything down and restructure; so the solutions they create using it operate well with the existing ones.
Creating the Interface
Once the connection to the data source has been established, it provides two ways to build an application: Canvas apps, which allow for full control of the layout and design, and Model-driven apps, which concentrate on data structures and preconfigured user interfaces. The drag-and-drop editor is most useful for users; nontechnical people; basically, they can visually lay out interface elements such as forms, buttons, and galleries without writing code. This, in turn, allows designers to quickly prototype their ideas, iterate based on feedback, and ensure that their final product not only serves the purpose but is also very user-friendly.
Business Logic Application
Adding logic is yet another way to make an app dynamic. In Power Apps, they created this business logic using Power Fx-formulas quite similar to Excel-that are, in fact, familiar to many business users. Power Fx allows developers and non-developers to trigger event actions to carry out validation, data inputs, or interact with other actions in response to users clicking; for example, if conditions are not met, they can hide certain fields from view, or automatically calculate a value for users. Hence, Power Apps enable applications to implement and verify complex business logic without resorting to the somewhat expensive bare-metal programming.
Integration with Power Automate
Another big advantage of Microsoft Power Apps is automation with Power Automate. What is Power Automate used for? Most often for automating repetitive tasks like sending requests for approval, updating records in CRM, or generating real-time reports. Power Automate can work inside an app, and when combined with Power Apps, it helps streamline workflows and eliminate manual steps. So, for example, with Power Apps, as soon as a form gets submitted, an automated process can start: the process might include emailing a manager, creating a new record in Dynamics 365, updating a SharePoint list, all without needing a human to follow up.
Testing and Deployment
Before you go live with an application, Power Apps has the in-built capabilities for testing and simulation. The creators will simulate the different user interactions going on with data flow and ensure that triggers for automation are working well. Roll out to targeted user groups or to the whole organization is seamless once the application meets the agreed standard: such controlled release helps to minimize disruptions and ensures critical feedback for further enhancement prior to formal launch.
User Access and Permissions
Security is built into every layer of Power Apps. Administrators can assign access and permissions to users on the basis of roles, ensuring the protection of sensitive data. This restricts the authorization only to view, edit, or administer a particular part of an application. Role-based access protects information and boosts usability; employees then see only what is pertinent to their current job function and that keeps interfaces free from clutter and reduces risks of errors.
Read More: How a Power Apps Consultant Can Boost Your App Development Speed?
Why Use Power Apps for Business?
Why use the Power Apps for business? Because Power Apps enables organizations to innovate faster, reduce costs and empower more people to build solutions. This very practical tool combines the low-code accessibility, enterprise-grade security, and the possibilities offered via its integration with the Microsoft ecosystem, that apply mutually to companies of all sizes.
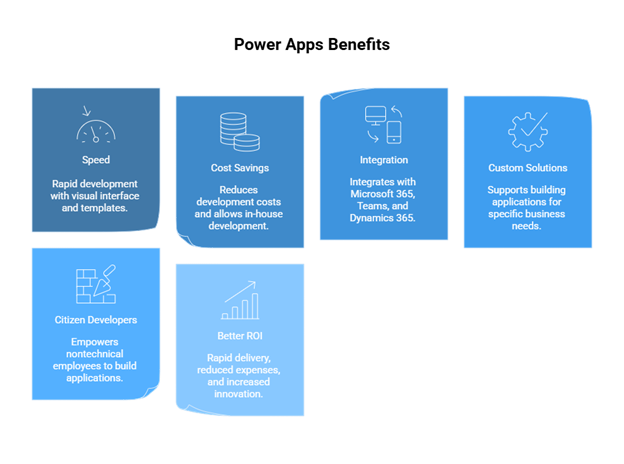
Speed up Application Development
Microsoft Power Apps offers a very short time to market for building full-fledged business applications through a visual interface, drag-and-drop design, and rich pre-built templates. For months, it takes just a few days or maybe several hours for a business to deploy an application into production. Those rapid deliveries help organizations react to the market needs in a fast-paced manner, design pilot solutions to test, and improve their approved application without delay.
Saving Costs
Power Apps reduces the heavy investments of personal fully-coded solutions and, hence, the high total cost of technology development. It allows companies to use in-house developers to develop their apps instead of paying expensive third-party developers to build its applications for every single project. A subscription-based license structure makes it possible for organizations to pay for what they use, meaning easier cost forecasts. Maintenance costs came down after the release of quick changes and few lines of code for each one. The accumulation of these savings over an extended period will allow a business to divert more income toward strategic growth initiatives besides relying on a decent share of custom applications.
Power Apps Integration
Integration stands as one of the most significant advantages for Microsoft Power Apps. It can have smooth and very tight integrations with Microsoft 365, Teams, Dynamics 365, and a bunch of third-party applications. This makes it a delightful option for unifying digital workflows. Through
built-in connectors, businesses can connect their applications directly to key data sources so that information from one system flows seamlessly across others. For example, an app created with Microsoft Power Apps could pull in customer data from Dynamics 365, show real-time reports in Teams, and trigger automated workflows in Power Automate, all with zero manual input. Such integration eliminates various problems and minimizes redundant data, which further improves the workflow.
Custom Solutions at Scale
Small departments with very specific requirements or an enterprise-wide large-scale installation; Microsoft Power Apps can support building applications that cater to very specific business needs. The main advantage lies in the flexibility of the platform wherein organizations can commence on a smaller scale, testing the solution, before scaling it across departments or global teams without rebuilding from the ground up. This eliminates the risk of applications becoming ineffective or irrelevant as the business evolves. From field service management to complex approval workflows, these apps offer the ability to cater to unique operational requirements without compromising on efficiency or security.
Empowerment for Citizen Developers
One of the most transformative features of the platform is that employees outside of the IT development bloField can be empowered. With Power Apps, nontechnical employees, sometimes called ‘citizen developers,’ can have their own secure and functional applications built for daily workflows. Therefore, it opens app development to innovation arising from the ranks, enabling those closest to business issues to execute solutions themselves. In the meantime, the IT group can lay down governance, data policies, and security standards so that all apps meet organizational standards while allowing room for innovation and agility.
Better ROI
The combined benefit of rapid delivery, reduced development expenses, integration, and an increase in staff innovation translates to an extremely equivalent value gain for Microsoft Power Apps. As a result of the rapid development and low-cost dependence on shopping grants, this platform serves to save more money but also improve productivity and enhance the operational efficiency framework. Employees now spend less time doing repetitive manual jobs and more time on strategic initiatives. However, in due course, Power Apps ends up making profit for itself and is thought to powerfully contribute to scaling business growth, enhancing customer experience, and upholding current standing in the fast-paced digital economy.
Microsoft Power Apps in the Microsoft Power Platform Ecosystem
Microsoft Power Apps sits at the heart of the Microsoft Power Platform, a suite of low-code/no-code tools provided to organizations for application development, workflow automation, data analysis, and creation of intelligent virtual agents. The tools together offer an end-to-end ecosystem to achieve the solution of business problems more efficiently and at scale.
Power Automate
Power Automate works hand-in-hand with Power Apps to eliminate manual intervention and quicken business processes. For example, an app designed to capture sales leads might also kick off a workflow that sends notifications, updates CRM records, and schedules follow-up activities autonomously. This very deep integration keeps proces
connecting with hundreds of services outside Microsoft, Power Automate takes Power Apps beyond a simple interface and acts as the head node of complex, multi-step workflows.
Power BI
The synergistic Power BI and Microsoft Power Apps offer enterprises the ability to expedite decisions. As an example, build an inventory tracking app using Power Apps, and then embed a Power BI dashboard to showcase stock trends in real-time. Decision-makers from the app interface can drill down into details for any specific data point and immediately decide on the actions to take. The gap between problem recognition and implementation of a solution gets reduced owing to this integration.
Power Virtual Agents
Integration of Power Virtual Agents in Power Apps enhances user experience through conversational interfaces. A helpdesk app, for instance, can have a chatbot that gives employees directions through troubleshooting steps or processes their leave requests. This deployment reduces pressure on support teams while providing instant and personalized assistance to users within their applications themselves.
Dataverse
Microsoft Dataverse acts as the common data backbone for Power Apps and other Power Platform tools. It securely stores structured and unstructured data under the application of standardized schemas so that apps can share information without any friction. By employing Dataverse, both developers and citizen developers can sidestep the challenge of having to deal with a different database for every app. It further supports complex business rules, relationships, and role-based security to restrict unauthorized users from peeping into sensitive information.
Cross-App Synergy
Because of their synergy, the Microsoft Power Platform expresses maximum power. For example, collecting customer satisfaction feedback through Microsoft Power Apps might be followed up on with Power Automate sending surveys; meanwhile, Power BI analyzes the results, and Power Virtual Agents respond to common customer queries, all without having to custom-code a single line. Doing so destroys silos, eliminates duplicated effort, and ensures a consistent user interface.
Consulting Support
While the Power Platform is poised to be one of the easiest tools to learn and implement, many organizations benefit from Power Platform Consulting Services. Experts can help businesses set an architecture that supports highest scalability, is compliant with security, and has performance optimization. Additionally, they provide training on best practices for the internal teams so that Microsoft Power Apps projects survive into the future.
Simplify App Development with Power Apps
Power Apps Development Best Practices
Best practices in Power Apps development guarantee secure, scalable, and maintainable applications built using Microsoft Power Apps. These best practices enable organizations to reap the full benefits of the platform while averting various roadblocks. Whether you are creating a small departmental application or building a large enterprise-wide application, the best practices will apply.
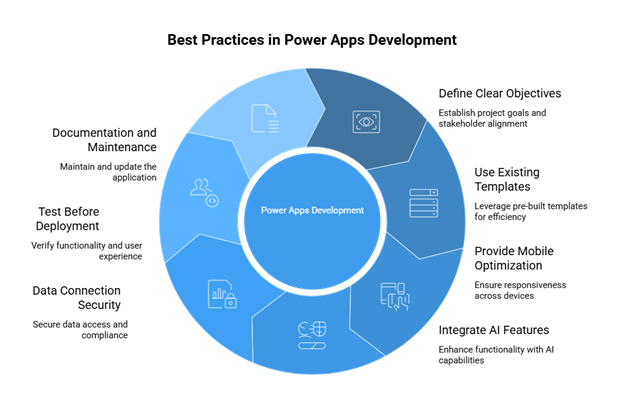
Define Clear Objectives
At the genesis of any Microsoft Power Apps project, it must be clear what issue the application is meant to solve. Without a clearly defined objective, development tends to stray toward fruitless features and complexity that do not deliver intrinsic value. First, engage stakeholders in discussions that revolve around pain points, expected results, and metrics of success. These documented business objectives should thus channel all involved, from the key decision-makers to the application developers to ensure that everybody shares the same vision. Clarity in objectives provides a smooth pathway for making decisions, leaves no room for scope creep, and prevents costly revisions later in the process. Focusing on the objectives makes it easier for the team to come with a solution quickly that has a greater impact.
Use Existing Templates
Taking advantage of the library of pre-built templates is one of the quickest ways to begin development in Microsoft Power Apps. The templates are varied and can cover anything from time schedules to reporting expenses, customer service, or inventory management. Numerous teams now arrange some customization of the templates to meet their workflows, branding, and data sources instead of creating an app from scratch. This is a huge time-saving process, helps keep the UI consistent across many apps, and enables businesses to deliver working tools in a swift manner without waiting for long stretches of custom coding.
Provide Mobile Optimization
As more and more employees go mobile with their smartphones and tablets, mobile users must always be kept in focus while creating their Microsoft Power Apps solution. Responsive layouts maintain that applications will look perfect and function smoothly across all devices whether it is used in portrait or landscape mode. Adaptive controls, scalable font sizes, and navigation
designed for finger interaction aid in boosting usability on a reduced screen. Testing the app on various devices in the lead-up to deployment could uncover many hiccups regarding layout and performance, which would otherwise detract from the user experience. Mobile optimization of the interface will garnish adoption rates while empowering employees even while on the road.
Integrate AI Features
Combine the Microsoft AI Builder with Power Apps, which lets developers and business users add intelligent features within their solutions. Such features may include automated form processing, sentiment analysis on customer feedback, or predictive modeling influenced by historical trends. Because an AI-engineered app goes farther in interacting with end users and anticipating user needs and providing data-driven insights, this naturally increases user engagement in the day-to-day value-giving operations of the app. For example, a service request app may predict the urgency of an issue and route tickets accordingly, which would save time for both employees and customers.
Data Connection Security
Security should be considered a paramount topic on any Microsoft Power Apps project. Maximum data access should be determined for each role to minimize unauthorized usage. Role-based permissions can be established natively within the Dataverse or with the data source on the other end of the connection. Power Apps can also join forces with Microsoft Entra ID (previously Azure Active Directory) for authentication and identity services at enterprise-level quality. The processes secure sensitive business data while also making sure that the security policies’ line of compliance is upheld. Data connection audits shall regularly require changes in relevance of access control checks with the varying needs of the organization.
Test Before Deployment
Testing a solution is a very important step before claiming to roll it out across an organization. Power Apps have built-in tools used to simulate user interactions, verify workflow logic, and generate test reports for performance in various scenarios. These test implementations can go for years, allowing extended feedback from just a few from an interested group of users concerning the app’s usability, effectiveness, and reliability. Conference proceedings include almost-funded issues that may be addressed before the general rollout in order to oversee the experiences of widespread adoption. The well-tested app would be trusted by end-users and would provide great value from day one.
Documentation and Maintenance
Each Microsoft Power Apps solution should have Documentation that explains its intent, functionality, data sources, and maintenance procedures. It stands as a handy reference for any subsequent updates or troubleshooting, regardless of whether the original developers or a new group is handling it. Proper documentation accelerates the integration process for new personnel and fosters project uniformity. After the launch, on the other hand, keep upgrading works, so the app remains compatible with changes to Power Apps itself, the linked services, and changing business requirements – thus, guaranteeing a long life.
Low-Code Power Apps and the Future of App Development
Microsoft Power Apps is a major player of the low-code Power Apps movement, and it enables a professional developer or a business user to develop applications with no or minimal coding work.Due to this shift, organizations are now fast-tracking innovation with digital solutions, making it far less expensive and accessible than traditional software Developoment.
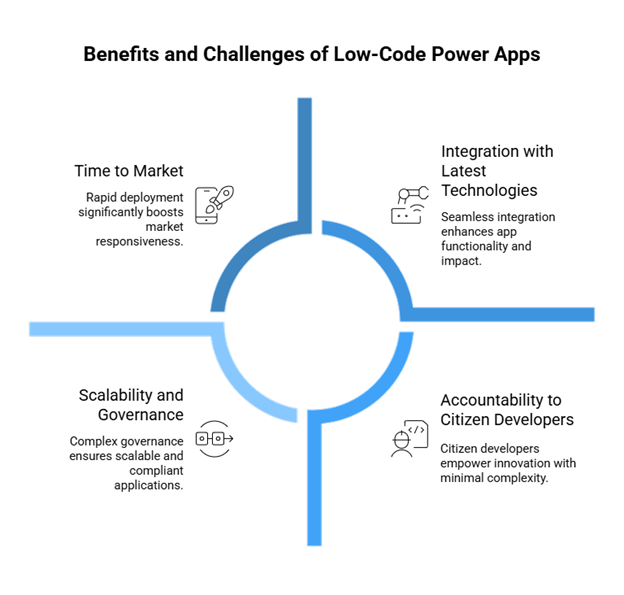
The Rise of Low-Code/No-Code Platforms
Platforms like Power Apps permit users to create applications through a drag-and-drop interface and visual logic, which considerably lowers the development complexities. Fostering app creation among the populace has given these teams-the ones who comprehend their problems best-often non-developers, to participate in assembling the solutions they need.
Time to Market
Projects that used to take months of arduous development can now be integrated in weeks, in some instances even days, with the aid of Microsoft Power Apps. This capability allows organizations to swiftly respond to transformations brought by markets, internal needs, or demands of customers, thereby winning in the competition.
Reducing Cost
Custom software development is expensive to run. Multiply an external developer or an agency in the mix to inflate the bill further. Using Power Apps, a business can cut down on costs with reusable components, built-in connectors, and ease of maintenance. Also, low-code can prevent the unforeseen expenses that may result from developer shortages or changes in project requirements.
Accountability to Citizen Developers
The end is near for application development being IT-bound forever. Employees in departments such as HR, finance, and operations are seriously challenged by MPower Apps to develop custom solutions all by themselves. Thus, citizen developers could come up in a matter of days, with added support from IT concerning security and compliance.
Integration with the Latest Technologies
The low-code platforms are evolving along with the latest features. Microsoft Power Apps makes AI capabilities, cloud integration, and IoT connectivity more accessible. For instance, a manufacturing app can employ AI Builder to forecast equipment failure, with data flowing directly into the app from IoT sensors in real time.
Scalability and Governance
Governance becomes critical when an increasing number of low-code applications are deployed in organizations. Power Apps helps in balancing agile innovation from the risks of data leakage and non-compliance as they provide centralized administration, data policies, and role-based access control. This balance between agility and oversight will be key to future adoption.
The Future Outlook
Keeping an eye on Microsoft Power Apps, it is obvious that this framework will influence and drive the next decade of digital transformation: more organizations are to resort to low-code tools in bridging talent gaps, fulfilling demands for custom solutions, and integrating advanced technologies. As the platform evolves, it shall continue to tear apart the distinction between business users and professional developers in a joint effort for software creation.
Conclusion
With Power Apps, businesses can quickly develop powerful custom applications with very little coding. It shortens the timeframe between service demand generation and technical implementation, thus fueling innovation faster, better integration, and enhanced productivity for all. With AI automation and low-code capabilities, it provides freedom and control in both small teams and large corporations. As digital adoption is accelerating in industrial sectors, Microsoft Power Apps has a distinguished position among representing platforms in terms of cost-effectiveness, scalability, and future-readiness. Businesses that adopt it nowadays will have a leg up to change, compete, and prosper in a fast-paced world. Harnessing it is a business imperative.
If you are looking for Power Platform Consulting Services, visit us here.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are Power Apps?
Power Apps is a low-code platform for app development, giving businesses the advantage of developing custom applications at a very rapid pace. Power Apps allows both technically gifted and non-technical users to design, build, and deploy solutions without requiring any complex programming knowledge.
Q2. What features stand out in Power Apps?
Some of the key features of Power Apps include drag-and-drop interface, more than 400 data connectors, and AI Builder integration. Other functions include role-based security, working with desktop apps, and mobile apps, giving it flexibility for many different business requirements.
Q3. How does the Microsoft Power Platform aid app development?
The Microsoft Power Platform integrates Power Apps, Power Automate, Power BI, and Power Virtual Agents into one whole environment, wherein organizations can build applications, automate their workflows, analyze their data, and create chatbots within the same ecosystem.
Q4. What are the advantages of using Power Apps for business application development?
Power Apps for business application development helps reduce development time, lessen cost, and streamline workflow efficiency and resulting innovation. Another important benefit is that it scales to grow with the needs of the organization.
Q5. What is an AI Builder in Power Apps?
AI Builder is a set of capabilities within Power Apps, the platform allows app makers to add artificial intelligence without writing code. It can be used to process forms, classify images, predict outcomes, and analyze sentiment to make applications smarter and more useful.
Recent Posts
- How Businesses Design Custom AI Solutions to Solve Complex Operational Challenges?
- How to Choose the Right AI Solutions Provider for your Company?
- Stop Paying for Logs You Don’t Use: The SaaS Guide to Smarter Azure Monitoring Services
- Top 7 AI Tools for Web Development in 2026
- CI/CD with Azure DevOps: A Practical Guide to Designing Secure and Reliable Pipelines
















